- Your program should read a floppy disk image provided here:
- Your program should accept the following commands and convert
them into the corresponding function calls:
| COMMAND |
FUNCTION CALL |
| load image |
int fd_load(char *image) |
| ls |
int fd_ls() |
| cd dir |
int fd_cd(char *directory) |
| rm file |
int fd_rm(char *name) |
- Disk Geometry (CHS) and Logical Block Addressing (LBA):
- Cylinders (Tracks), Heads (Surfaces), Sectors, Blocks.
A 1.44 MB floppy disk has 80 cylinders
(0-79), 2 heads (0-1) and 18 sectors (1-18),
total number of blocks = 80*2*18 = 2880
- Logical sector I on track T, head H, sector S is located at
I = S-1 + T*(heads*sectorsPerTrack) + H*sectorsPerTrack
- MS-DOS Floppy Disk Organization:
- Reserved Region (Boot Sector)
- FAT Region
- Root Directory Region
- File and Directory Data Region
- Snapshots captured from khexedit:
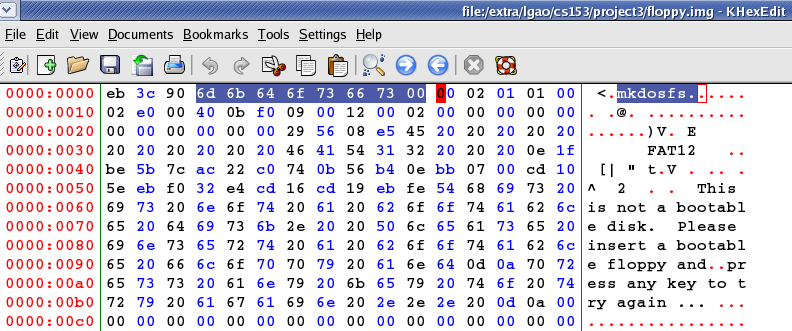
- The boot sector:
- First sector in the first FAT:

- The root directory:
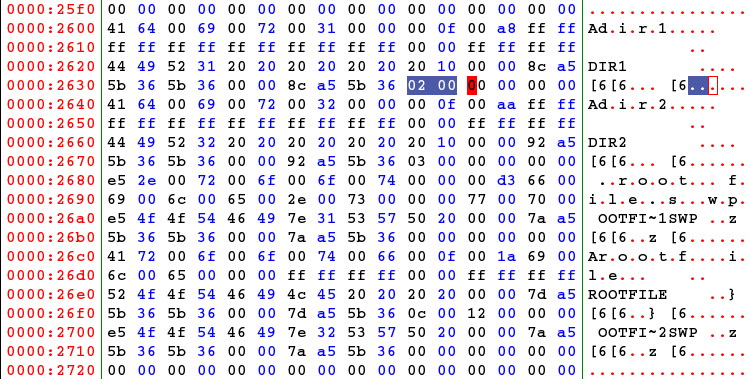
- The directory named "dir1":
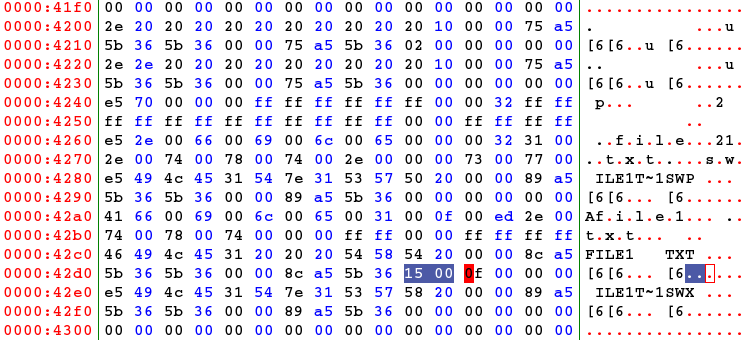
- The file named "file1":

- How to calculate the logical sector number of a sub-directory?
- Take the Starting cluster number at 0x1A of the
directory entry
- offset = (31 + starting_cluster_number) * bytesPerSector
- 31 = 1 (boot sector) + 18 (2 FATs, 9 sectors each) + 14 (224
root directory entries, 32 bytes each) - 2 (logical sector 33
correspond to FAT cluster 2)
|